Week 05 - Artificial Intelligence
- Lami'ah Nosarka

- Nov 3, 2023
- 2 min read

01/11/2023 - 08/11/2023
This week focused on #ArtificialIntelligence and covered the following topics:
Differentiate between AI, ML and Deep Learning
AI Logic – State Space Search
Explain Classification problems in ML
Understand the use of Recommender Systems
Activity #1
This activity requires us to search for examples where we can apply machine learning, and some examples for deep learning.
Machine Learning Definition:
Machine learning is an application of Artificial Intelligence that provides systems the ability to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
Examples of where machine learning can be applied:
Image Recognition | One of the key applications in machine learning is image recognition. It's used to identify objects or specific features in digital images and has wider applications like pattern recognition, face detection, and facial recognition. |
Speech Recognition | Machine learning software has the ability to convert spoken words into numerical representations based on the speech signal. Speech recognition, facilitated by such technology, finds widespread use in popular applications like Amazon's Alexa, Apple's Siri, and functionalities within Google Maps. |
Predict Traffic Patterns | Looking at Google Maps as an example; as users input their location into the application, it initiates the collection of extensive traffic-related data. This data includes current traffic conditions and patterns, allowing the system to formulate predictions about future traffic scenarios. Based on this analysis, Google Maps then identifies the most efficient route to the user's destination, aiming to provide the quickest and most optimal travel path. |
E-commerce Product Recommendations | E-commerce sites often use machine learning to recommend products. They track what users buy, look at, and add to their carts to suggest items that match their interests, using AI to personalize these recommendations. |
Catching Email Spam | Email services use ML algorithms to filter and sort incoming emails, making sure spam emails goes straight to the spam folder. |
Deep Learning Definition:
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning in Artificial Intelligence (AI) that has networks capable of learning based on complex learning algorithms especially useful for large data.
Customer experience (CX) | Deep learning powers chatbots and is set to improve customer experience across businesses, increasing satisfaction as it evolves further. |
Text generation | Machines are learning the grammar and style of a given text to generate new content that matches the original in spelling, grammar, and style automatically. |
Aerospace and military | Deep learning plays a role in identifying objects from satellite imagery, helping pinpoint areas of interest and determining safe or hazardous zones for military operations. |
Industrial automation | Deep learning boosts worker safety in places like factories and warehouses. It helps automate systems to detect when a person or object gets too close to machinery, preventing accidents. |
Adding colour | Deep learning models now enable the addition of color to black-and-white photos and videos. This task, previously laborious and manual, has been significantly streamlined. |
Activity #2
For this activity we will look into depth-first search and find one advantage and one disadvantage of depth-first search algorithms.
What is Depth-First Search?
DFS, short for Depth-First Search, is an algorithm for moving through trees or graphs. It begins at the starting point (usually the root node) and keeps exploring down a path until it reaches the end. If it hits a dead-end, it goes back to the last point where it had other options to explore. This method uses a "last in, first out" approach, managed through a stack data structure.
1 Advantage of DFS:
When depth-first search discovers a solution without extensively exploring a path, it significantly reduces the time and space it requires.
1 Disadvantage of DFS:
The algorithm does not search further after finding a solution resulting in the possibility of missing other solutions (if there are more than one)
Activity #3
This activity requires us to use a Teachable Machine with two (or more) objects/ classes as well as give a brief discussion of what Machine Learning is and a few applications of it.
Here is a demonstration of how a teachable machine works:
Activity #4
This activity requires us to find out whether the new point, (5, 2), belongs to X or O.
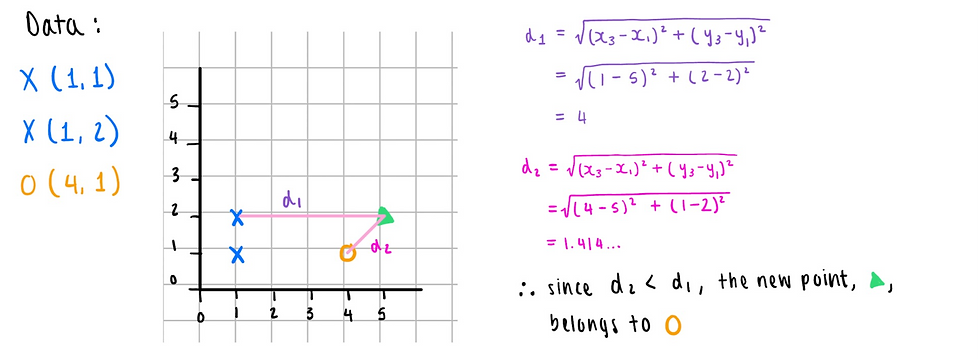
Activity #5
This activity requires us to use #ChatGPT to find out how it works.
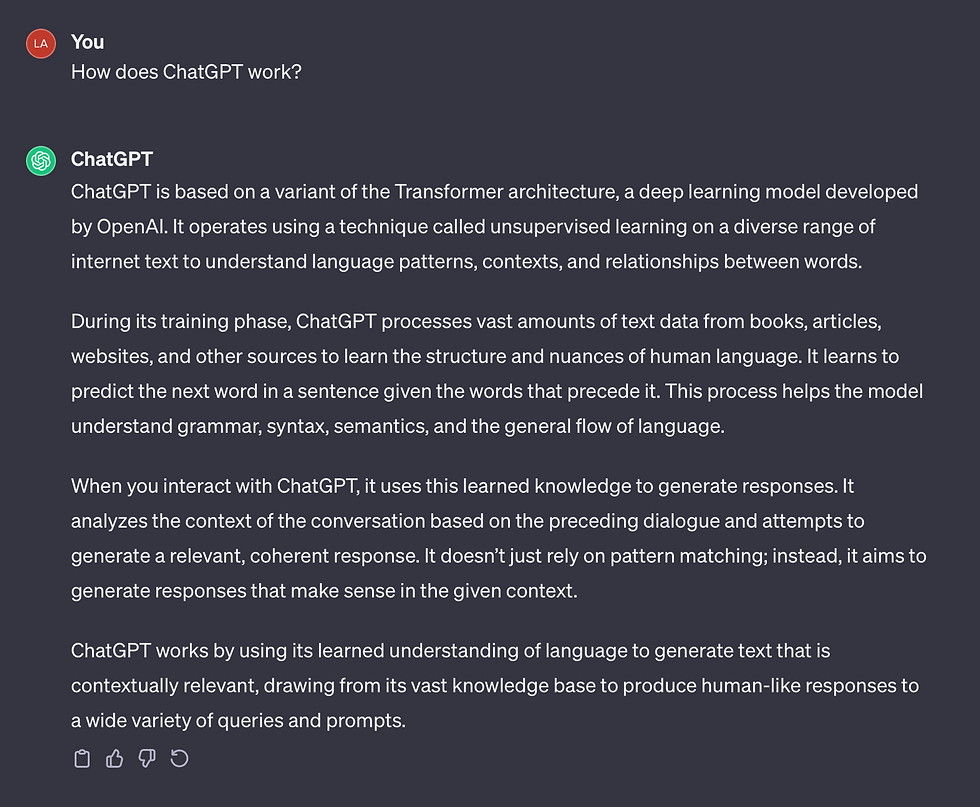

After going through each response, I prefer the first explanation as it is more in-depth but still easy to understand. I think the second explanation would be suitable for a person who does not have a basic understanding of IT.
References:




Comments